Introduction of “Design Thinking Practice Training

TDC SOFT Inc. offers a variety of UX design-related training programs. In this issue, we would like to introduce “Design Thinking Practical Training” for creating and realizing new value. In this training, participants learn the mindset and basic concepts required for design thinking, and then acquire practical skills through workshops.
- What is Design Thinking?
- Background of the need for design thinking
- Design Thinking and UX Design
- What you will learn through the training
- Training Flow
- Point 1: Workshops directly related to practical skills
- Point ➁ Don't be afraid to fail or make mistakes! Know the importance of an exploratory approach
- Voices of Training Participants
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is an approach that focuses on problem solving and innovation, and aims to solve problems by gaining a deep understanding of user needs and challenges.
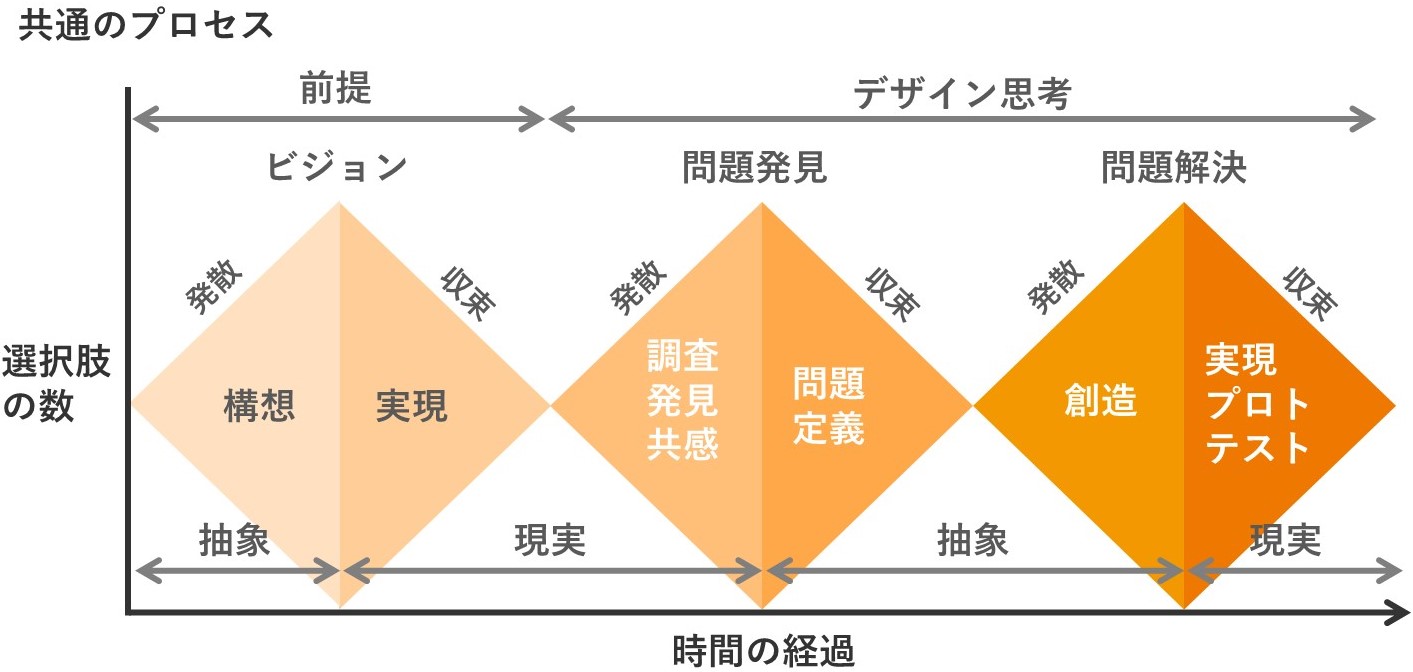
Various organizations and companies have defined the process of Design Thinking. The six steps are “problem definition” to find latent needs and insights from the problems and issues discovered, “creation” to come up with ideas for the defined problems, and “realization, prototyping, and testing” to realize the ideas, have people actually try them out, and get feedback. The process is carried out with the cooperation of various members of the team. For those who want to understand Design Thinking in more detail, there is a basic course on Design Thinking on YouTube. Please take a look at it as well.
Background of the need for design thinking
In the past, products and services were typically developed by focusing on technology and product features. However, in today’s rapidly changing and increasingly competitive marketplace, it has become increasingly important to focus on the needs and challenges of users. Therefore, the design thinking approach that focuses on the user has come to be recognized as a useful way of thinking for all those involved in product and service development.
Design Thinking and UX Design
What is the difference between “design thinking” and “UX design”? Here is a brief explanation.
Design Thinking is 0 → 1
“0 → 1” refers to the process of generating new ideas and solutions. Design thinking is a method for redefining problems and understanding user perspectives, and focuses on the stage of creatively deriving new ideas and concepts.
UX design is 1→10
“1→10” refers to the stage of design realization and optimization. UX design is a process where the ideas generated through design thinking UX design focuses on the stage of materializing ideas into actual products and services and devising the best possible user experience. Design Thinking is used in the early stages of creating new ideas and solutions or redefining problems, while UX Design is used in the stages of implementation and optimization. We hope you can see that Design Thinking and UX Design are complementary.
What you will learn through the training
Design thinking is sometimes viewed as a “theory for generating ideas” or a “method for generating novel ideas,” but this is not the case. Architect Peter Lowe defined design thinking as “a way of thinking for innovation based on human-centered design.

There are four important points in design thinking: First, it is human-centered and important to understand people’s feelings; second, innovation (creating new satisfaction or bringing new value) is also possible by combining or improving what is already there; third, it verbalizes designers’ everyday thinking and behavior, so that non-designers can easily put it into practice; fourth, it focuses on the mindset, thinking, and behavior of designers, so that they can put it into practice, The fourth is that it is important to focus on the mindset, thinking, and actions of designers, and to translate this mindset into actual actions. TDC SOFT Inc. offers “Design Thinking Practice Training” with the hope that these important points will be understood through practice.
Training Flow
This training program is a three-day training course, the majority of which is in the form of practical workshops.

Point 1: Workshops directly related to practical skills
The curriculum that is especially designed to be practical is the research on the first day and the problem definition on the second day. In these two processes, it is necessary to shake off stereotypes, become a beginner, and dig deeper into information, switching between various angles and perspectives with curiosity. In addition, since just discussing the issue within the team will result in an empty theory on the table, it is important to practice by asking someone, going to places where users are, and observing.
About the Survey
Many people think of research as quantitative research (breadth), in which statistical trends and patterns are found from a large amount of information obtained from surveys and other sources to gain insights and discoveries about users, but in design thinking, the emphasis is on qualitative research (depth) to gain insights that lead to latent needs and insights about the target audience. In the work of this training course, we also use qualitative research to gain insights into the potential needs and insights of the target audience.
In this training course, teams are asked to conduct qualitative research. First, a hypothesis is formulated and a research plan is drawn up. After that, the flow of the fieldwork is to conduct action observation surveys and depth interviews. When conducting depth interviews for the first time, it is often the case that only superficial information is gathered and no insights into the latent needs and insights of the user are gained. We would like to share some of our beginners’ mistakes with you on our Youtube channel.
The survey process involves explaining the necessary mindset and creating a survey plan with the team. After an interview exercise, the actual interview is conducted. These processes are similar to those used in our survey work. Since the instructor facilitates each task, the curriculum is designed so that even first-time participants can learn the survey flow well.
Problem Definition
The main purpose of problem definition is to discover latent needs and insights that users themselves are unaware of. To achieve this, we select important points from the information obtained in the survey, dig deeper into these points, connect them with other information, and find meaning by interpreting their relationships to find latent needs and insights. In our training work, we spend more than half a day defining the problem. We use a framework called ladder tree, which allows for abstraction (why?) and concretization (how?). and concretization (how?) and then digging deeper, exchanging opinions with team members.
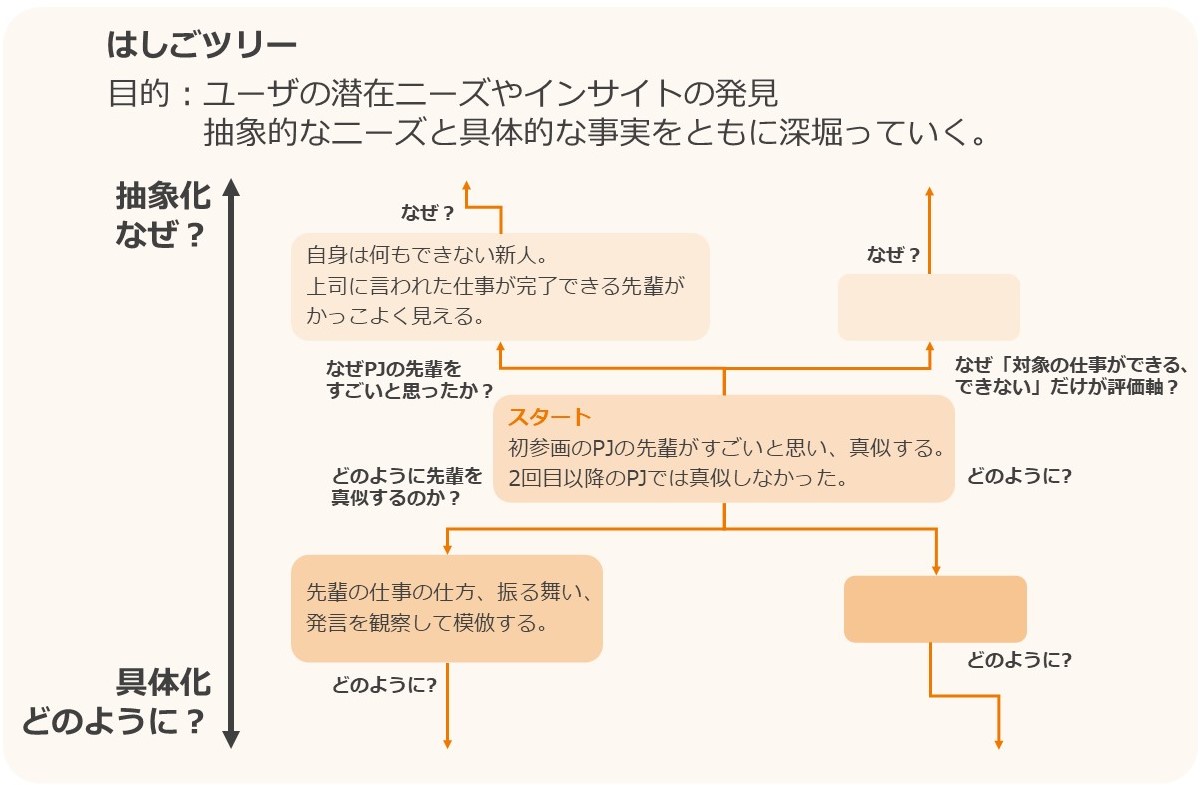
After a while after starting, some teams will start thinking too deeply about users and their brains will become fatigued, gradually running out of new perspectives and angles, or they will summarize in easy words and come up with only insights that they have heard somewhere before. If a team is stuck, the instructor will organize the discussion points, ask appropriate questions, and facilitate the team to come up with new insights.
Participants also commented that they had never thought so much about users before, and that they were able to find insights that they had not been able to notice before. This is the first time we have received comments such as “I was able to find insights that I did not notice before.
Point ➁ Don't be afraid to fail or make mistakes! Know the importance of an exploratory approach

An “exploratory approach” is an approach to finding new ideas and solutions in an exploratory manner, without relying on existing knowledge or formulaic methods, within a limited time frame, because the correct answer is not known. In this training course, participants will formulate a hypothesis, create a prototype, test it, and evaluate it during the three-day curriculum.
In addition, the participants are required to produce output within a limited time frame, and many of them feel uneasy about the degree of completion. However, in the lecture, it is explained that there is no need to accept such a situation as a problem or to be too pessimistic. In the actual workshop, through repeated trial and error, participants gain insights from their failures, discover discoveries that were overlooked in conventional approaches, and discover new perspectives that even the lecturers are surprised to see.
Furthermore, discussions with teammates with different backgrounds and skills are also very effective, and participants realize that approaching the same problem from different perspectives can generate unexpected ideas and concepts. Through the training, participants will understand the advantages of the exploratory approach, and the experience gained through practice will surely be useful in their future work and projects.
Voices of Training Participants
Although the training lasted several days, a great number of participants said that it was a fulfilling experience at the end. Many participants said, “There is no point in acquiring knowledge alone. I want to put it into practice immediately.
The following are some of the results of a questionnaire from the participants.
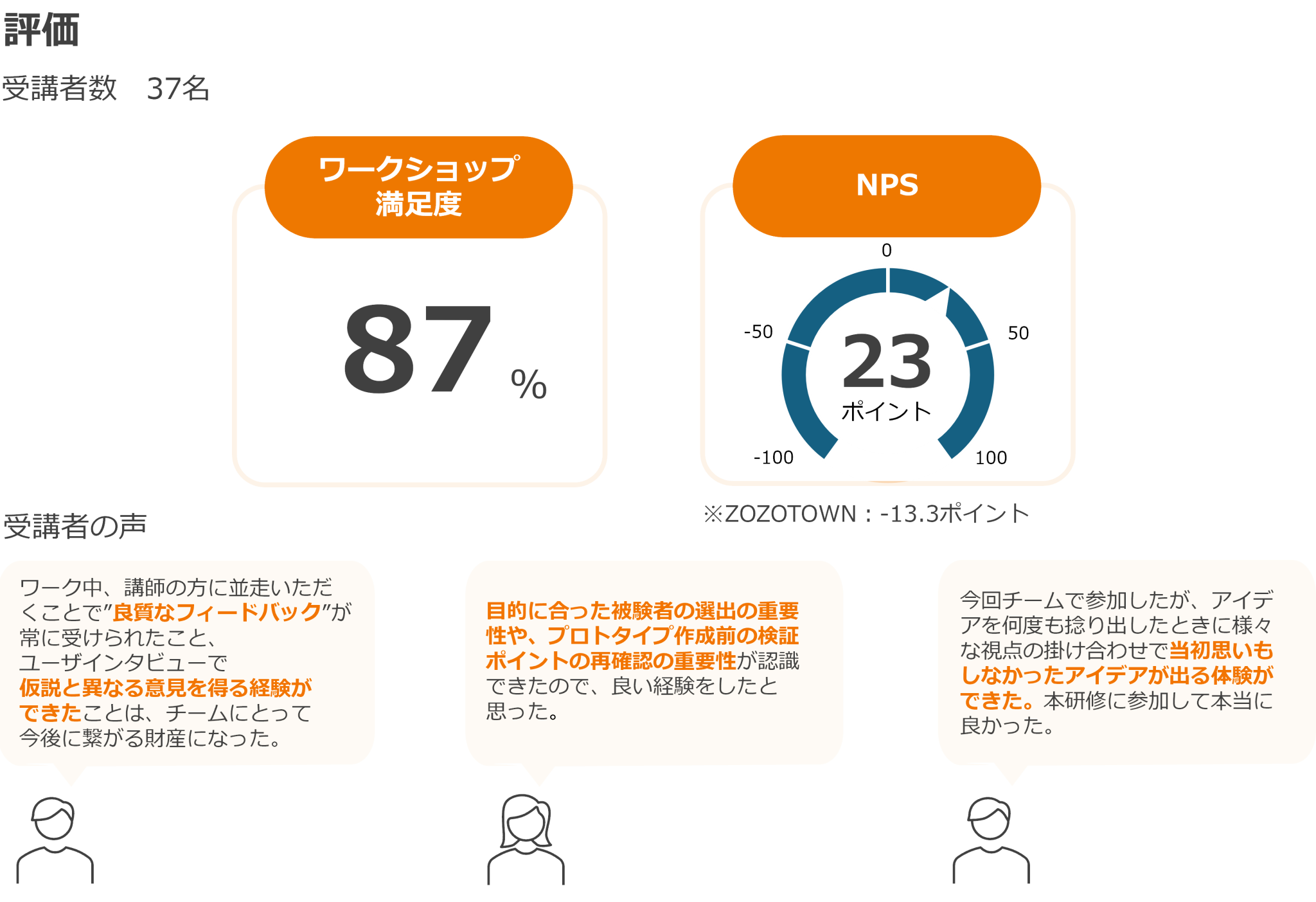
TDC SOFT Inc. listens to the participants=users and continues to make kaizen efforts to ensure that the training is something that participants can make use of in the real world. In addition to “Design Thinking Practice Training,” TDC SOFT Inc. also provides training related to UX design and UI design. We also have a lineup of training programs in the fields of Agile and security.
If you are interested in our services, please contact us. Click the button below to contact us.
Technologies Used

UX Design
We provide support using a variety of UX design techniques to help you deliver an experience that truly delights you and your users.
